
AWS, Google Cloud Platform, and Microsoft Azure are locked in a fierce three-way battle for cloud supremacy. There are various aspects to consider while choosing a public cloud service provider. A full comparison of AWS, GCP, and Azure will be provided in this blog.
Cloud computing has progressed rapidly. It’s no longer an issue of whether or not to use cloud computing; it’s instead a matter of choosing which cloud platform to use.
Microsoft, Google, and Amazon are the three most popular cloud computing companies today, each with its cloud-based storage platforms — Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Amazon Web Services (AWS).
The IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) and PaaS (Platform as a Service) market niches are dominated by these platforms.
Overview of a cloud platform:
There are several smaller cloud providers on the market that might be a suitable fit for your organization.
The current cloud service market is dominated by a few large suppliers who are well-positioned to take advantage of public cloud adoption. Azure, Google Cloud Platform, and Amazon Web Services are the three most popular cloud providers.
The Establishment of AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud:
Amazon Web Services (AWS)

AWS was first made public in 2006, with services like Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3), and others. By 2009, Amazon CloudFront, Content Delivery Network (CDN), and more formally joined the AWS Cloud Computing Service offerings, as well as Elastic Block Store (EBS).
Amazon Web Services is a subsidiary of Amazon.com that offers a subscription-based on-demand Cloud Computing platform to people, businesses, and governments.
Amazon Web Services is the cloud market’s oldest and most experienced company. As one of the first cloud providers, it has a larger user base, as well as higher levels of trust and reliability.
Google Cloud Platform

Google, which began operations in 2008, has only recently emerged as a serious competitor to both AWS and Azure. GCP offers IaaS and PaaS, as well as a serverless platform with computing, storage, databases, different networking options, and database and IoT administration, similar to the other two platforms.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is a set of Cloud Computing services provided by Google that run on the same infrastructure that Google uses internally for its end-user products like Google Search, YouTube, and others.
Microsoft Azure

Microsoft Azure, formerly known as Azure, was introduced in 2010 to provide organizations with a reliable Cloud Computing platform.
Azure, created by Microsoft Web Services was introduced barely four years after Amazon’s initial entry into the cloud computing market, has quickly established itself as AWS’s most significant direct competitor and the world’s second most popular cloud platform.
AWS vs. GCP vs. Azure: Benefits and Drawbacks
Every solution can be described by its own set of pros and cons. Let’s have a look at what we’ve got.
- AWS pros & cons
Pros:
- Exceptional technical capabilities
Amazon Web Services is a platform that covers a wide range of cloud-based operations, offering easily expandable cloud space with only the client’s individual needs and vision limiting its expansion possibilities.
- Adaptive features
The vast AWS platform offers a wide range of services, tools, and other capabilities, handling anything from everyday management to in-depth data analytics and smart predictions.
- Data transmission is stable
AWS assists in the efficient avoidance of data loss during storage or server
data transmission, removing plenty of associated risks.
Cons:
- Emphasis on the public cloud
In the absence of out-of-the-box private and hybrid cloud options, enterprise-oriented capacities are fairly limited, making AWS an alternative to be carefully examined for internal corporate use.
- Confusing costs
A non-clear long-term pricing policy with changeable conditions and uncertain conditions for additional budget strategizing is one of the most prominent complaints among organizations that prefer AWS.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP) pros & cons
Pros:
- The Kubernetes standard
GCP can manage big data analytics and ML-powered data processing due to in-depth containerization, resulting in faster and better field operation results.
- Scaling and load balancing
Google is a competent provider, with well-run data centers and quick-to-respond services in general.
- Google Ecosystem
Companies looking for cloud options employ a variety of Google software solutions, making the gradual adoption of GCP performance-enhancing.
Cons:
- There is a lack of corporate agenda
Due to the system’s more novel, start-up-oriented nature, GCP’s application area is constrained, with the infrastructure supplying some market-defining cloud capabilities that can’t fully serve all-in-one corporate cloud purposes.
- Limitations of technology
Only PHP, Java, and Google Go are supported by GCP’s App Engine, limiting the full variety of compatible software methods and solutions.
- Costly charges
Working with GCP can be costly in terms of managing data downloads and covering support costs (the average monthly support subscription is $150)
- Microsoft Azure pros & cons
Pros:
- Microsoft’s power
The massive cloud vendor essentially adapts all of its on-premise gist (including software solutions like.NET, SQL Server, Office, and so on) for cloud-based use, providing clients with the best of Microsoft’s offerings.
- An ecosystem that is widely distributed
the majority of firms use some Microsoft software solutions here and there, and Azure comes in as a highly versatile alternative because it is easily integrated with all of them.
- Performance of the company
Azure is a good choice for most businesses, allowing them to create custom cloud infrastructures based on Microsoft’s tested capabilities.
- Cons:
- Integrations with third-party services
Microsoft is easily integrated with similar solutions; but, when merging with non-Microsoft products, there may be substantial issues.
- Flexibility is restricted
If the workflow is primarily Microsoft-based, Azure can assist create a robust business system, but the total platform adaptability is limited by the inability to entirely customize the cloud architecture both inside and outside.
- Storage Technologies
AWS Storage
Amazon’s Simple Storage Service is an industry-standard protocol that is supported by the majority of major cloud providers (e.g. GCP). The Elastic Block System from Amazon also provides big block storage (EBS).
Storage Gateway from Amazon is a hybrid cloud service that lets you use both a local cache and the cloud. If your data storage requirements exceed those of an ordinary company, Amazon’s Elastic File Storage solution allows you to scale up as needed.
To reduce downtime and make the move to AWS easier, AWS offers SQL-supported databases and a data migration service.
Google Cloud Platform Storage
The storage options offered by Google are very simple, with cloud storage and persistent disk storage rounding out the options. However, because GCP supports both SQL and no-SQL databases, what is offered is dependable and comprehensive.
Cloud SQL is a relational database service for MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server that is fully managed. Cloud Datastore is a NoSQL database that is extremely scalable.
Microsoft Azure Storage
Azure provides a range of storage cloud options to meet a variety of business requirements. Larger enterprises with high data storage demands might choose Azure Data Lake Storage and Queue Storage.
Azure has the most SQL-based databases, with three different formats to choose from. Even more intriguing is Azure’s hybrid approach, which includes the Server Stretch database, which allows organizations to use Microsoft SQL Server for on-premises operations while also storing data in the cloud.
- Data Analytics
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
AWS provides the following data analysis tools: Elastic MapReduce for data processing;
- Data Pipeline for easy data management;
- Kinesis Streams for real-time data streaming;
- Kinesis Firehose for large-scale data input;
- Quick Sight for in-depth data analysis.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Google’s platform makes use of another unique data analytics solution called BigQuery, which is a fully managed enterprise data warehouse that makes accessing and storing large datasets simple, due to tools like:
- Cloud Data Fusion;
- Cloud Dataflow;
- Cloud BigTable;
- Cloud Dataprep, etc.
Microsoft Azure
Providing an innovative Azure Synapse Analytics service for data
integration, warehousing, and analysis, as well as features like:
- HDInsight,
- Power BI,
- Azure Machine Learning,
- Azure Cognitive Services,
- Azure Data Factory, etc
- Availability Zone: AWS Vs. GCP Vs. Azure
The fact that AWS was the first in the cloud sector has already been proven, implying that they have had more time to create and expand their network. As a result, AWS hosts in multiple locations throughout the world. Azure and GCP both have various locations around the world, but the variation is in the number of availability zones they have.
- AWS now offers 66 availability zones, with an additional 12 on the way.
- Google Cloud Platform is now available in 20 worldwide areas, with three more on the way.
- Azure is accessible in 140 countries and is available in 54 regions throughout the world.
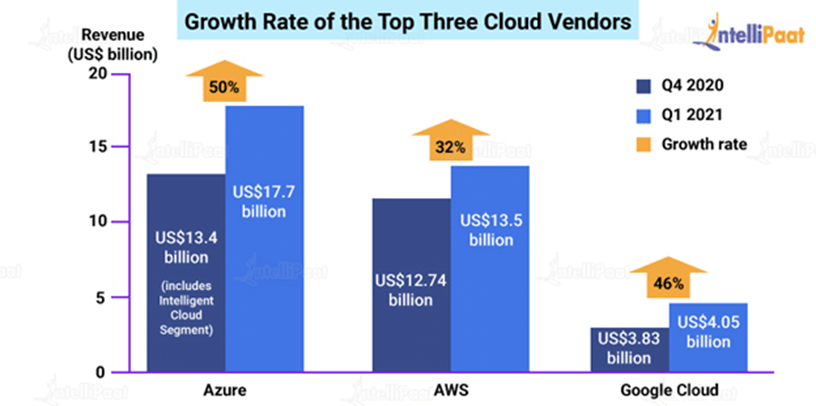
- Market shares and Growth rate: AWS Vs. GCP Vs. Azure
Microsoft’s Azure cloud revenue has been noted to beat both AWS and Google Cloud combined, according to announced quarterly earnings for 2021.
According to the fiscal earnings report, Microsoft’s Azure cloud-topped its competitors with commercial-cloud revenue of US$17.7 billion (a 50 percent increase over the previous quarter). While Amazon’s AWS claimed US$13.5 billion in cloud revenue for the quarter (up 32% from the previous quarter), Google Cloud only recorded US$4.05 billion.
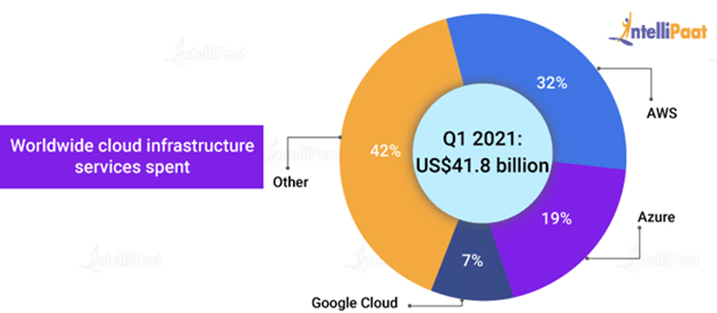
According to Canalys, the worldwide cloud market increased 35 percent to $41.8 billion in the first quarter of 2021. AWS accounts for 32% of the market, with Azure accounting for 19% and Google accounting for 7%.
- Compliance and Cloud Security
- AWS security
Because Amazon is the oldest – and most experienced – cloud service provider, it has dealt with a wider range of problems and found solutions to them. Isolation via security groups (firewalls) and granular IAM, as well as vulnerability evaluation via AWS Inspector, API activity monitoring, threat information via Guard Duty, and data loss prevention are all available from Amazon.
The only problem appears to be related to AWS’ age, as many of the aforementioned security mechanisms were created separately and before large-scale cloud integration platforms were on the radar.
- Google Cloud Platform security
Many experts consider GCP to be a successful security bridge between AWS and Azure. While segregating projects and defaulting to more secure options, Google has taken care to maintain centralized security access.
However, GCP’s security features and security specialists do not compare to those of AWS, although the Cloud Security Command Center is robust.
- Azure security
Whereas AWS’s strengths come from its isolation (you’ll have to configure security protocols for each account separately), Azure’s come from its central security system, which can be managed from a single location. However, with fewer separation and controls in place to monitor interface and API activity throughout the entire organization, internal risks become more likely.
Enterprises also fault Azure for inconsistent documentation of compliance and defaulting to less-secure configurations.
- Comparison of Prices
- AWS Pricing
Amazon’s pricing structure has been described as “so complicated that you’ll need a third-party tool to handle it.” Amazon however, provide a free 12-month trial of 750 hours per month on its EC2 services, as well as a 75 percent discount for a 1-3-year commitment.
- GCP Pricing
Google has certainly attempted to learn from its competitors’ failures by implementing a simple cost-per-second model. Additionally, GCP’s free tier gives one free micro-instance per month for the first year, a $300 credit for a year of service, and a 30% discount for long-term use.
- Azure Pricing
Azure users frequently utilize a third-party tool to control costs, which is similar to how AWS users do. Also similar to AWS, Azure offers a free tier that includes 12 months of 750hr/month Virtual Machines and a steep discount for a 1-3 year commitment.
- Who Uses AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure?
- Because AWS is the oldest player in the cloud business, it has a larger user base and community support. As a result, AWS has a larger number of high-profile and well-known clients, including Netflix, Airbnb, Unilever, BMW, Samsung, MI, Zynga, and others.
- Google Cloud, on the other hand, uses the same infrastructure as Google Search and YouTube, and as a result, many high-end enterprises trust Google Cloud. HSBC, PayPal, 20th Century Fox, Bloomberg, Dominos, and others are among Google Cloud’s many clients.
- With time, Azure is getting a larger number of high-profile customers. Azure currently boasts about 80% of Fortune 500 firms as customers. Johnson Controls, Polycom, Fujifilm, HP, Honeywell, Apple, and others are among its key clients.
- Dilemma of Choosing
AWS simplifies large-scale scalability, allowing you to avoid and remove plenty of usual risks, errors, and wasted time. When it comes to cost management, it’s adaptable and connects well with third-party services.
However, it is a system that, to function correctly, necessitates the use of profiled specialists, establishes a felt price for resources consumed, and only offers enterprise functionality as a paid add-on.
GCP offers extensive data storage and analytics capabilities, as well as seamless connectivity with a variety of other Google services and affordable, flexible pricing methods.
The Google ecosystem’s confines, on the other hand, may be regarded as a technological limitation, as the programming languages available are limited, and there are regional restrictions as well.
Microsoft Azure is easy to use, simple, and comprehensive right out of the box. It can be simply supplemented with a variety of MS-integrable services and tools. It may also be appropriate for businesses of any size and assist in achieving cost-effectiveness.
However, you should observe your data transfer intensity with this one to avoid extra costs, and it may not fit your needs in the long run if you don’t put enough customized effort into configuring and managing it if you are a large enterprise that requires a large all-in-one solution.
Conclusion:
Amazon Web Services is a leading cloud platform with significant computing power acquired through a wide range of solutions for businesses of all sizes.
However, considering that Azure and GCP are continuously working their way up the top cloud providers list, it’s difficult to determine how long AWS will have the title of leading cloud provider.
Even though AWS has the benefit of being the first of its kind, Azure and GCP each offer their own set of advantages.
Several firms that utilize Microsoft tools choose Azure cloud since it is simple to integrate MS tools with Azure cloud. The only reason consumers should choose GCP is that it offers the best pricing plan for the infrastructure that runs Google Search and YouTube.
So, in the end, it’s preferable to state that it’s not about picking the greatest cloud providers, but rather selecting the finest cloud provider for your requirements.

Very informative
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you. https://accounts.binance.com/en/register-person?ref=P9L9FQKY
Your article gave me a lot of inspiration, I hope you can explain your point of view in more detail, because I have some doubts, thank you.
I really like reading through a post that can make men and women think. Also, thank you for allowing me to comment!
I very delighted to find this internet site on bing, just what I was searching for as well saved to fav
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
yes what do you wanna know!