In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, the ability to extract valuable insights from vast amounts of data has become an essential competitive advantage. This is where Business Intelligence (BI) comes into play, revolutionizing the way organizations make informed decisions and drive growth.
In this blog post, we’ll embark on a journey to demystify the world of Business Intelligence.
This blog Covers:
What Is Business Intelligence?
- Business Intelligence Concepts
- Importance
- Application
- Benefits
- Components
What Is Business Intelligence?
Business intelligence (BI) refers to the processes, technologies, and tools that use to gather, analyze, and transform raw data into meaningful insights. It involves data collection and examination from various sources within a company or external to it, to make informed business decisions and improve overall performance.
BI encompasses various activities, including data mining, data warehousing, reporting, analytics, and visualization. By utilizing BI, organizations can extract valuable information from large and complex data sets, identify patterns and trends, and comprehend their business operations, customers, and market conditions.
Process
The process of business intelligence involves several interconnected stages that collectively aim to turn raw data into valuable insights.
Here are the steps involved in the business intelligence process:
Data Collection: The first step is to identify and gather relevant data from various sources, both internal and external to the organization. This data can include sales records, customer data, financial data, market research, social media data, and more.
Data Integration: Once the data is collected, it should be consolidated and integrated into a unified format. This involves transforming and combining data from different sources, resolving inconsistencies, and ensuring data quality and accuracy.
Data Warehousing: In this step, the integrated data is stored in a central repository called a data warehouse. The data warehouse is designed to support efficient querying and analysis, and it typically involves organizing the data into structured tables or cubes.
Data Analysis: With the data warehouse in place, analysts and business users can start exploring the data and performing various analysis techniques. This can include querying the data using SQL or other programming languages, applying statistical analysis, performing data mining and predictive modeling, and conducting multidimensional analysis to identify patterns, trends, and correlations within the data.
Reporting and Visualization: Once the analysis is complete, the insights interface through reports, dashboards, and visualizations. This step involves presenting the findings clearly and concisely that are easily understandable by business users. Visualizations can include charts, graphs, maps, and other graphical representations of the data.
Decision-Making: The insights derived from the analysis and visualization stages are used to inform decision-making processes within the organization. Business users, managers, and executives can leverage the insights to make informed and data-driven decisions, such as identifying market opportunities, optimizing operations, improving customer satisfaction, or developing strategic plans.
Monitoring and Iteration: Business intelligence is an iterative process, and it requires continuous monitoring and refinement. Organizations should track the performance of their decisions and initiatives, gather feedback, and incorporate new data to refine their analysis and improve future decision-making.
In business intelligence, it’s crucial to have the right technology and tools, such as data integration tools, data warehouses, analytical software, and visualization platforms. These tools facilitate the collection, integration, analysis, and presentation of data, enabling organizations to extract meaningful insights and drive better business outcomes.
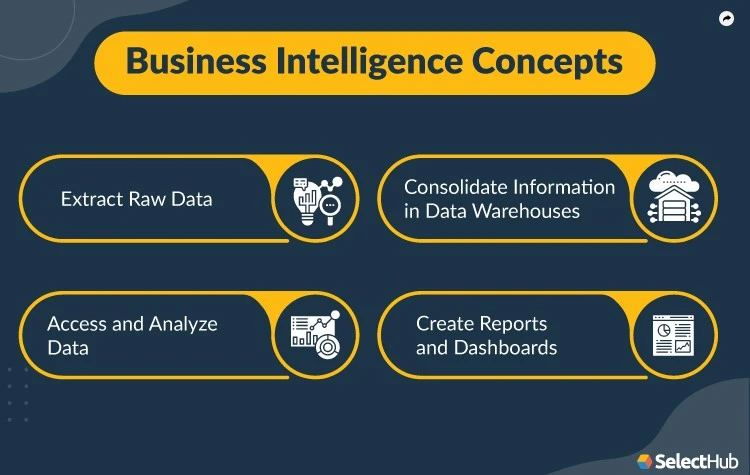
Concepts of business intelligence
The four basic concepts of business intelligence
The four concepts of business intelligence (BI), “Four Pillars” or “Four C’s” concepts represent the fundamental aspects of BI that organizations need to consider when implementing a business intelligence strategy.
The four concepts are as follows:
Content: Content refers to the data collected and analyzed within the BI system. It encompasses all the relevant information gathered from various sources, such as internal databases, external data providers, and other data repositories. Quality, completeness, and accuracy are crucial for obtaining reliable insights and making informed decisions.
Context: Context refers to the understanding of the business environment in which the BI system operates. It involves considering the specific needs, goals, challenges, industry trends, market conditions, and regulatory factors that impact decision-making. Understanding the context helps to interpret the data accurately and align the BI initiatives with the organization’s strategic objectives.
Consolidation: Consolidation refers to integrating and combining data from multiple sources to create a unified and comprehensive view of the organization’s information. It involves data integration, transformation, and cleansing activities to ensure that the data is consistent, standardized, and reliable. Consolidating data enables effective analysis and reporting by providing a single source of truth for decision-making.
Collaboration: Collaboration refers to fostering a culture of collaboration and knowledge sharing within the organization. BI is not just about generating insights; it is also about disseminating those insights to the right stakeholders at the right time. Organizations actively share reports, dashboards, and visualizations with relevant teams, facilitate discussions around the data, and actively promote a data-driven decision-making culture across departments and levels.
These four concepts work together to establish a solid foundation for a successful BI implementation. By focusing on content, context, consolidation, and collaboration, organizations can ensure that their BI initiatives depend on accurate and relevant data, are aligned with business objectives, provide holistic information, and encourage collaboration and knowledge sharing among stakeholders.
Applications
Business intelligence (BI) has several applications across various industries and sectors. Here are some common applications of business intelligence:
Performance Monitoring: BI helps organizations monitor their performance by tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics. It enables businesses to analyze and measure their performance against predefined targets and benchmarks, identify areas of improvement, and take proactive actions to enhance performance.
Financial Analysis: BI provides financial insights by analyzing financial data, such as revenue, expenses, profitability, and cash flow. It helps organizations in budgeting, financial forecasting, cost analysis, identifying cost-saving opportunities, and optimizing financial decision-making processes.
Sales and Marketing Analytics: BI helps organizations analyze sales and marketing data to gain insights into customer behavior, sales trends, market segmentation, and campaign performance. It enables businesses to optimize marketing strategies, identify target customers, improve customer retention, and increase sales effectiveness.
Customer Analytics: BI enables organizations to analyze customer data and comprehend customer preferences, buying patterns, and satisfaction levels. It helps identify customer segments, customer churn, personalize marketing campaigns, and improve overall customer experience.
Supply Chain and Operations Management: BI supports supply chain and operations management by providing real-time visibility into inventory levels, production processes, and logistics. It helps optimize inventory management, reduce costs, improve supply chain efficiency, and identify bottlenecks.
Risk Management: BI enables organizations to assess and manage risks by analyzing data from various sources, such as financial data, market data, and historical records. It helps to identify potential risks, predict future risks, and implement risk mitigation strategies to protect the organization from adverse events.
Competitive Intelligence: BI assists organizations in gathering and analyzing data about competitors, market trends, and industry benchmarks. It assists in benchmarking performance against competitors, identifying market opportunities, and making informed decisions to gain a competitive advantage.
HR Analytics: BI supports human resources departments in analyzing employee data, such as recruitment metrics, performance evaluations, and employee engagement surveys. It helps optimize workforce planning, identify skill gaps, measure employee performance, and improve talent management strategies.
These are just a few examples of how business intelligence is applied across different areas of an organization. The versatility of BI allows organizations to leverage data to gain valuable insights and make data-driven decisions that drive efficiency, innovation, and competitive advantage.
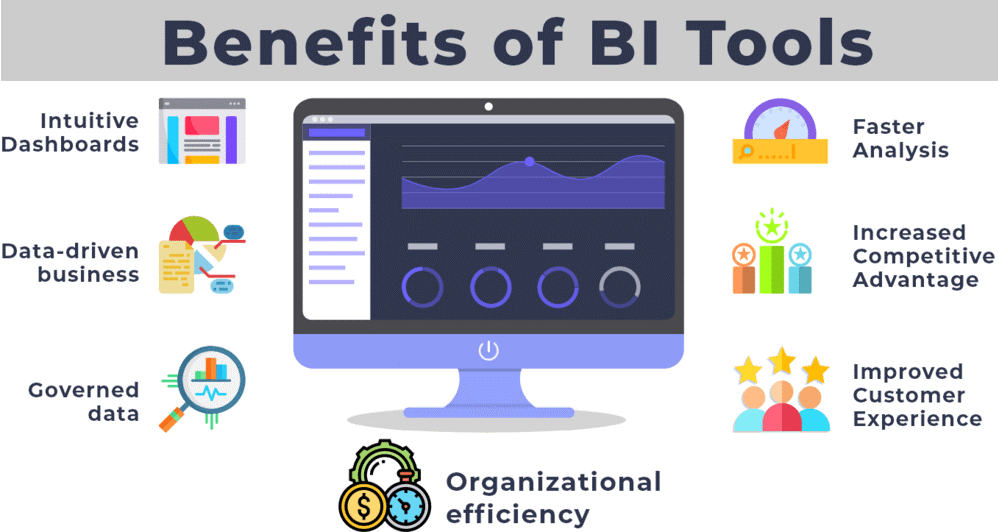
Primary Benefits
Implementing a business intelligence (BI) strategy offers several primary benefits for organizations. Here are some of the key advantages:
Data-Driven Decision Making: BI enables organizations to make informed and data-driven decisions. By collecting, analyzing, and visualizing data, BI provides valuable insights that help understand market trends, customer behavior, operational efficiency, and other critical factors. This leads to better decision-making processes and reduces reliance on intuition or guesswork.
Improved Operational Efficiency: BI helps organizations identify inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement within their operations. By analyzing data related to processes, resource utilization, and performance metrics, organizations optimize, streamline workflows, and enhance overall efficiency.
Enhanced Strategic Planning: BI supports strategic planning by providing accurate and timely information. Organizations can analyze historical data, market trends, and competitive intelligence to develop effective strategies, identify growth opportunities, and mitigate risks. BI enables organizations to align their goals and initiatives with market demands and make data-driven decisions for long-term success.
Increased Competitive Advantage: BI provides organizations with a competitive advantage by enabling them to stay ahead of market trends and make proactive decisions. By analyzing customer data, market data, and competitor intelligence, organizations can identify emerging opportunities, anticipate customer needs, and develop targeted marketing strategies to gain a competitive edge.
Improved Customer Experience: BI allows organizations to comprehend their customers. By analyzing customer data, purchase history, preferences, and feedback, organizations can personalize marketing campaigns, improve customer service, and enhance the overall customer experience. This leads to increased customer satisfaction, loyalty, and retention.
Better Resource Allocation: BI helps organizations optimize resource allocation by providing insights into resource utilization, demand forecasting, and cost analysis. This enables organizations to allocate resources effectively, identify areas of waste or inefficiency, and optimize budget allocation for maximum ROI.
Real-Time Monitoring and Reporting: BI enables real-time monitoring and reporting of key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics. Organizations can track performance, identify deviations from targets, and take immediate corrective actions. Real-time reporting facilitates quick decision-making and enables organizations to respond swiftly to changing market conditions.
Enhanced Data Governance and Compliance: BI promotes better data governance practices by ensuring data quality, consistency, and security. It helps organizations comply with regulations and standards by providing a centralized and controlled environment for data access, analysis, and reporting.
In conclusion, business intelligence (BI) is a powerful discipline that encompasses concepts, components, and applications aimed at leveraging data to drive informed decision-making and achieve organizational success. The concepts of content, context, consolidation, and collaboration form the foundation of BI, ensuring that organizations have access to accurate and relevant data within the right business context, consolidated in a unified format, and fostering a collaborative environment for knowledge sharing.
I simply wanted to construct a simple comment in order to appreciate you for the fabulous information you are giving out at this site. My rather long internet research has finally been rewarded with brilliant concept to write about with my friends and classmates. I ‘d assert that most of us website visitors actually are definitely fortunate to dwell in a very good community with many brilliant professionals with great tactics. I feel very much happy to have discovered your entire web pages and look forward to really more fabulous minutes reading here. Thanks a lot once more for everything.