Robotic process automation (RPA) is a rapidly growing technology transforming the finance back-office. RPA software robots can automate repetitive, rules-based tasks, allowing human employees to focus on more strategic and value-added work.

What is RPA?
RPA stands for Robotic Process Automation. It’s a software robots that uses software robots or “bots” to automate rule-based, repetitive tasks that are typically performed by humans. These bots mimic human actions by interacting with applications and systems just as a human user would but in a more efficient, accurate, and consistent manner.
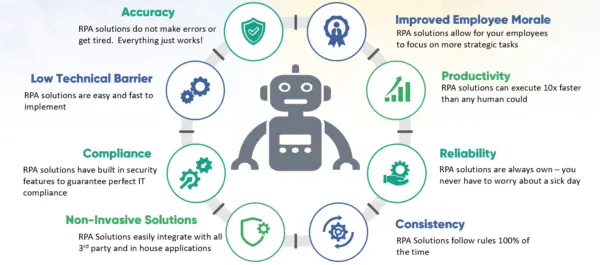
RPA is different from traditional automation in that it does not require extensive coding or complex integrations with existing systems. Instead, it operates at the user interface level, working with the front end of applications and using the same interfaces that humans use. This makes RPA relatively easy to implement and allows organizations to achieve automation quickly without disrupting their existing infrastructure.
RPA can be used to automate a wide range of back-office tasks, including:
- Data entry and processing
- Document management
- Compliance reporting
- Customer service
- IT support
By automating these tasks, RPA can help fintech industries in
Cost Savings: By automating manual and time-consuming processes, finance RPA reduces the need for human intervention, leading to cost savings in labor and operational expenses.
Error Reduction: It minimizes human error by executing tasks with precision and consistency. This leads to improved output quality and ensures accurate financial data.
Compliance and Audit Trail: RPA helps financial institutions comply with industry regulations and standards. By automating compliance checks and maintaining an audit trail of all processes, organizations can easily demonstrate adherence to requirements.
Efficiency in Repetitive Tasks: Finance departments often deal with repetitive tasks like data entry, reconciliation, and report generation. RPA automates these processes, improving overall departmental efficiency and freeing up staff to focus on more strategic activities.
Enhanced Risk Management: RPA enables real-time monitoring of transactions and alerts for potential risks. This proactive approach empowers organizations to address risk promptly and efficiently.
Effective Data Management: RPA automates the collection and integration of data from various sources, ensuring a more comprehensive and accurate analysis. This facilitates better decision-making processes.
In addition to these benefits, RPA can also help financial institutions to:
One of the most significant benefits of RPA is that it can help to elevate customer service. RPA can free up those representatives by automating many of the tasks, currently handled by customer service representatives, to focus on more complex and challenging issues. This can lead to faster resolution times, improved accuracy, and a more positive customer experience.
In fintech, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has proven to be a game-changer, with up to 80 % of rule-driven tasks being automated. This technology has found numerous use cases in the BFSI sector, given its strict regulations and high data quality and security. By leveraging RPA, financial organizations can capitalize on various opportunities to improve their processes and deliver better customer services.
Automation of Account Opening Process: RPA has revolutionized the account opening process, making it more accurate and efficient. By eliminating data conversion errors between the central banking system and new account requests, RPA ensures higher data quality within the organization. This results in quicker turnaround times, increased accuracy, and reduced costs.
Streamlining Client Onboarding: Client onboarding is often a complex and time-consuming due to regulatory requirements. RPA and AI in banking can simplify this process by extracting essential information from KYC documents and comparing it against the application data using optical character recognition (OCR) technology. This significantly reduces the risk of human errors, and saves time and effort for the staff.
Enhancing KYC and AML Procedures: RPA excels in handling data-intensive tasks, making it an ideal solution for automating Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) procedures. Whether automating manual tasks or detecting abnormal banking activities, RPA offers cost-effective and time-saving benefits compared to traditional approaches.
Generating Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs): Financial institutions regularly create SARs for fraudulent transactions, which involves manual review and data entry. RPA software can scan extensive compliance documents and populate SAR forms with relevant information, improving accuracy and reducing operational costs and cycle time.
Accelerating Mortgage Lending Processes: Mortgage lending is a crucial aspect of banking, but it often involves complex and time-consuming tasks. RPA can automate various lending processes, including credit arrangement, quality audit, and document processing. As a result, loan requests are handled faster, leading to increased customer satisfaction.
Speeding up Loan Underwriting: Loan underwriting has historically been a slow process, despite some automation efforts. RPA can further streamline this process, with virtual assistants reducing the turnaround time to as little as 15 minutes, enhancing overall efficiency.
Overall, RPA is a powerful technology that has the potential to transform the finance back-office and elevate customer service. As more and more fintech industries adopt RPA, we can expect to see even greater benefits in terms of cost savings, efficiency, accuracy, and customer satisfaction.
Here are some examples of how RPA is being used in the finance industry to transform back-office operations and elevate customer service:
- Bank of America is using RPA to automate the processing of loan applications. This has helped the bank to reduce the time it takes to process a loan application from 10 days to 2 days.
- JPMorgan Chase is using RPA to automate the reconciliation of customer accounts. This has helped the bank to reduce the number of errors in account reconciliation by 90%.
- Wells Fargo is using RPA to automate the processing of customer complaints. This has reduced the time it takes to resolve a customer complaint from 15 days to 5 days.
- These are just a few examples of how RPA is being used to transform the finance back-office and elevate customer service. As RPA technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative and impactful applications in the future.
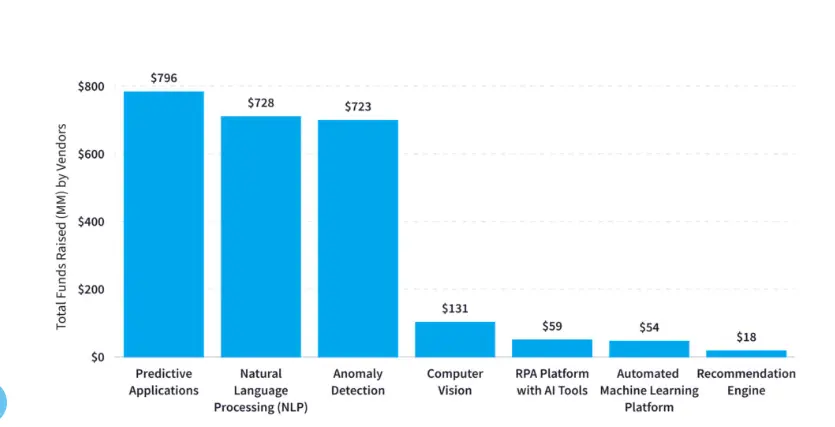
Conclusion
In conclusion, RPA has emerged as a game-changer in transforming finance back-office operations and elevating customer service in the financial industry. By automating repetitive tasks and streamlining processes, RPA enhances efficiency, reduces errors, and frees up valuable resources.
As financial institutions embrace RPA, they are better positioned to meet customer demands, deliver personalized experiences, and stay ahead in an increasingly competitive landscape. The future of finance is undoubtedly brighter with RPA driving innovation and customer-centricity to new heights.
